COMPOSITION
Key Points
- It represents a part-of relationship.
- In composition, both the entities are dependent on each other.
- When there is a composition between two entities, the composed object cannot exist without the other entity. For example, if order HAS-A line-items, then an order is a whole and line items are parts
- If an order is deleted then all corresponding line items for that order should be deleted.
- Favor Composition over Inheritance.
Program Example of Java Composition
Let us consider the following program that demonstrates the concept of composition.
Step 1:
First we create a class Bike in which we declare and define data members and methods:
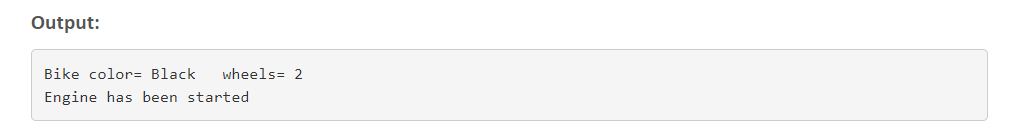
class Bike{// declaring data members and methodsprivate String color;private int wheels;public void bikeFeatures(){System.out.println("Bike Color= "+color + " wheels= " + wheels);}public void setColor(String color){this.color = color;}public void setwheels(int wheels){this.wheels = wheels;}}Step 2:
Second, we create a class Honda which extends the above class Bike. Here Honda class uses HondaEngine class object start() method via composition. Now we can say that Honda class HAS-A HondaEngine:
class Honda extends Bike
{//inherits all properties of bike classpublic void setStart(){HondaEngine e = new HondaEngine();e.start();}}The next step in this Java Composition program is
Step 3:
Third, we create a class HondaEngine through which we use this class object in above class Honda:
class HondaEngine
{public void start(){System.out.println("Engine has been started.");}public void stop(){System.out.println("Engine has been stopped.");}}The final step of this Java Composition Program
Step 4:
Fourth we create a class CompositionDemo in which we make an object of Honda class and initialized it:
class CompositionDemo
{public static void main(String[] args){Honda h = new Honda();h.setColor("Black");h.setwheels(2);h.bikeFeatures();h.setStart();}}