Arrays
In computer programming, an array is a collection of similar types of data. For example, if we want to store the names of 100 people then we can create an array of the string type that can store 100 names.
String[] array = new String[100];The number of values in the Java array is fixed. That is, the above array can not store more than 100 elements.
How to declare an array in Java?
In Java, here is how we can declare an array.
dataType[] arrayName;- dataType - it can be primitive data types like
int,char,double,byte, etc. or Java objects - arrayName - it is an identifier
For example,
double[] data;Here, data is an array that can hold values of type double.
But, how many elements can array this hold?
Good question! To define the number of elements that an array can hold, we have to allocate memory for the array in Java. For example,
// declare an array
double[] data;
// allocate memory
data = new Double[10];Here, the array can store 10 elements. We can also say that the size or length of the array is 10.
In Java, we can declare and allocate memory of an array in one single statement. For example,
double[] data = new double[10];How to Initialize Arrays in Java?
In Java, we can initialize arrays during declaration. For example,
//declare and initialize and array
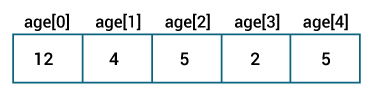
int[] age = {12, 4, 5, 2, 5};Here, we have created an array named age and initialized it with the values inside the curly brackets.
Note that we have not provided the size of the array. In this case, the Java compiler automatically specifies the size by counting the number of elements in the array (i.e. 5).
In the Java array, each memory location is associated with a number. The number is known as an array index. We can also initialize arrays in Java, using the index number. For example,
// declare an array
int[] age = new int[5];
// initialize array
age[0] = 12;
age[1] = 4;
age[2] = 5;
..Note:
- Array indices always start from 0. That is, the first element of an array is at index 0.
- If the size of an array is n, then the last element of the array will be at index n-1.
How to Access Elements of an Array in Java?
We can access the element of an array using the index number. Here is the syntax for accessing elements of an array,
// access array elements
array[index]Let's see an example of accessing array elements using index numbers.
Example: Access Array Elements
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] age = {12, 4, 5, 2, 5};
// access each array elements
System.out.println("Accessing Elements of Array:");
System.out.println("First Element: " + age[0]);
System.out.println("Second Element: " + age[1]);
System.out.println("Third Element: " + age[2]);
System.out.println("Fourth Element: " + age[3]);
System.out.println("Fifth Element: " + age[4]);
}
}Output
Accessing Elements of Array: First Element: 12 Second Element: 4 Third Element: 5 Fourth Element: 2 Fifth Element: 5
In the above example, notice that we are using the index number to access each element of the array.
We can use loops to access all the elements of the array at once.
Looping Through Array Elements
In Java, we can also loop through each element of the array. For example,
Example: Using For Loop
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] age = {12, 4, 5};
// loop through the array
// using for loop
System.out.println("Using for Loop:");
for(int i = 0; i < age.length; i++) {
System.out.println(age[i]);
}
}
}Output
Using for Loop: 12 4 5
In the above example, we are using the for Loop in Java to iterate through each element of the array. Notice the expression inside the loop,
age.lengthHere, we are using the length property of the array to get the size of the array.
We can also use the for-each loop to iterate through the elements of an array. For example,
Example: Using the for-each Loop
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] age = {12, 4, 5};
// loop through the array
// using for loop
System.out.println("Using for-each Loop:");
for(int a : age) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}Output
Using for-each Loop: 12 4 5
Example: Compute Sum and Average of Array Elements
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {2, -9, 0, 5, 12, -25, 22, 9, 8, 12};
int sum = 0;
Double average;
// access all elements using for each loop
// add each element in sum
for (int number: numbers) {
sum += number;
}
// get the total number of elements
int arrayLength = numbers.length;
// calculate the average
// convert the average from int to double
average = ((double)sum / (double)arrayLength);
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
System.out.println("Average = " + average);
}
}Output:
Sum = 36 Average = 3.6
In the above example, we have created an array of named numbers. We have used the for...each loop to access each element of the array.
Inside the loop, we are calculating the sum of each element. Notice the line,
int arrayLength = number.length;Here, we are using the length attribute of the array to calculate the size of the array. We then calculate the average using:
average = ((double)sum / (double)arrayLength);As you can see, we are converting the int value into double. This is called type casting in Java. To learn more about typecasting, visit Java Type Casting.
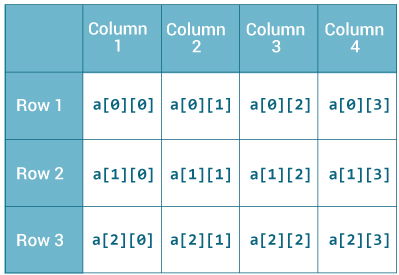
A multidimensional array is an array of arrays. Each element of a multidimensional array is an array itself. For example,
int[][] a = new int[3][4];Here, we have created a multidimensional array named a. It is a 2-dimensional array, that can hold a maximum of 12 elements,
Remember, Java uses zero-based indexing, that is, indexing of arrays in Java starts with 0 and not 1.
Let's take another example of the multidimensional array. This time we will be creating a 3-dimensional array. For example,
String[][][] data = new String[3][4][2];Here, data is a 3d array that can hold a maximum of 24 (3*4*2) elements of type String.
How to initialize a 2d array in Java?
Here is how we can initialize a 2-dimensional array in Java.
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};As we can see, each element of the multidimensional array is an array itself. And also, unlike C/C++, each row of the multidimensional array in Java can be of different lengths.
Example: 2-dimensional Array
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 2d array
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
// calculate the length of each row
System.out.println("Length of row 1: " + a[0].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 2: " + a[1].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 3: " + a[2].length);
}
}
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 2d array
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
// calculate the length of each row
System.out.println("Length of row 1: " + a[0].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 2: " + a[1].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 3: " + a[2].length);
}
}Output:
Length of row 1: 3 Length of row 2: 4 Length of row 3: 1
In the above example, we are creating a multidimensional array named a. Since each component of a multidimensional array is also an array (a[0], a[1] and a[2] are also arrays).